The devout and observant Christian is undoubtedly aware of the precarious state of the faith in our modern world and is becoming increasingly open to out-of-the-box solutions. One such possible solution is to take a cue from our bearded Amish neighbors and form rule-based religious communities—but maybe without the horse and buggy.
A brief peak at the current state of American Christianity should disabuse anybody of the notion that this is unnecessarily drastic.
America’s traditional Mainline Protestant denominations are bleeding out so quickly they will likely be gone within 20 years. That is not my prediction, but their own. The ELCA (the main Lutheran branch) projects they’ll only have 16,000 worshippers by 2041; the PCUSA (the main Presbyterian branch) lost almost 40% of their members in the last decade, causing one analyst to note, “At its current rate of shrinkage the PC(USA) will not exist in about 20 years;” and data for the Episcopal Church shows the same 20-year timeline until the denomination runs out of people in the pews.
Orthodox. Faithful. Free.
Sign up to get Crisis articles delivered to your inbox daily
More conservative denominations used to chuckle at these headlines and say, “If only they preached the Gospel instead of liberal activism, they’d be growing like us.” But they don’t say that anymore. The Southern Baptist Convention, the largest of the Evangelical churches, has lost 14% of their members since 2006; the Methodists are losing members while in the middle of a brutal split; and for Catholics, according to Bishop Robert Barron while speaking at the 2019 bishops’ annual conference, “Half the kids that we baptized and confirmed in the last 30 years are now ex-Catholics or unaffiliated.”
There is one major exception, though: the Amish—a mustard seed that is growing into a large tree in front of our eyes. The Amish arrived in the United States shortly after their founder, Jakob Ammann, split with the Mennonites in 1693 for being too lax on enforcing their communal rules, as laid out in the Dordrecht Confession of Faith. For the next 200 years, the Amish were just a few eccentric families in Pennsylvania that spoke an archaic Swiss German. By 1920, these few families had grown to 5,000 people and since then have doubled about every 15 to 20 years, including between 2000 and 2020 when they doubled to 351,000.
Unless something changes drastically within their culture, this doubling is projected to continue. One demographer, Lyman Stone, showed that at their current rate of growth, they will easily make up a majority of the United States in 200 years. This means the current moment may mark the halfway point between them arriving as a small band of friends and their inheriting the most powerful nation on the planet. They may seem like a backwards remnant of the past, but in reality, they will almost certainly play a major role in the future. This will become more evident after they soon dwarf more well-known churches like the Episcopalians and Lutherans. 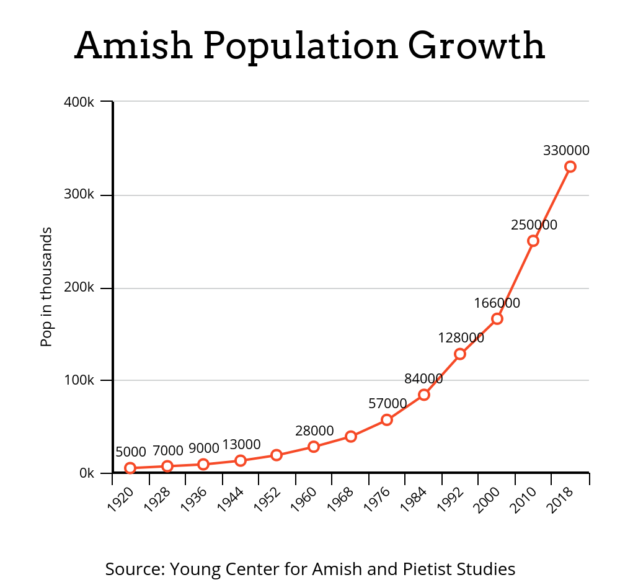 So, when virtually all other Christian groups are seeing plummeting, or at best stagnant, numbers, why are the Amish seeing growth like this? The answers people typically give are that they have a very high birth rate and an over 90% retention rate. But that’s like saying someone is wealthy because they made a lot of money and then saved most of it. It begs the question—how? How do they have such large families—with 6 or 7 children per woman—while the country at large has a below-replacement rate of 1.6 children? And how are they able to keep all those children within their communities?
So, when virtually all other Christian groups are seeing plummeting, or at best stagnant, numbers, why are the Amish seeing growth like this? The answers people typically give are that they have a very high birth rate and an over 90% retention rate. But that’s like saying someone is wealthy because they made a lot of money and then saved most of it. It begs the question—how? How do they have such large families—with 6 or 7 children per woman—while the country at large has a below-replacement rate of 1.6 children? And how are they able to keep all those children within their communities?
I believe it all comes down to one thing—the Code—or as the Amish call it, the Ordnung.
The Amish Ordnung is different in each community, but if it strays too far, other communities will no longer associate with that community; so there are limits. While outside observers will just see strict rules about hats and beards and technology use, the Amish see the glue that holds them together as a people.
It’s very important to realize that each rule is chosen as a group and with the goal of strengthening individual virtue (especially humility), family and community ties, and their faith.
As an example, most Amish communities don’t allow phones in their homes, but it’s not because they think phones are inherently evil and ban them completely. They often have shared phone booths at the end of the street to use when necessary and at their places of work. They just don’t have phones in the home because they believe it will take away from the purposes of a home—things like family bonding, chores, and recreation. Nobody who has sat in a room of family and friends all silently swiping at their phones can tell me their concern isn’t warranted.
They have similar rules limiting, and occasionally banning, other technologies like cars, computers, and electricity. These rules are agreed upon and enforced on everyone in the community. Those who repeatedly break the rules can find themselves excommunicated or shunned for a time. While it’s not uncommon for someone who disagrees strongly with one custom to find another community that doesn’t practice it, for the most part, as the 90% retention rate shows, people decide to follow the Ordnung and remain in the community.
The success of this model was discussed by Eric Kaufmann, a political-demography scholar at the University of London, in his provocative 2010 book, Shall the Religious Inherit the Earth?: Demography and Politics in the Twenty-first Century. Kaufmann noted the growth of groups like the Amish and the Haredi Jews (often called the Ultra-Orthodox) and attributed it to their birth rates and strong communities. Haredi Jews, for example, who also live by strict community codes, were only a few percentage points of the Israeli schools in 1960 but are now about a third of students, and he predicts they will very soon eclipse secular Jews. Haredi growth in Brooklyn, New York, is seeing similar growth, with high birth rates and retention.
“The ones who grow through proselytization, like the evangelicals, they don’t have this kind of explosive growth,” Kaufmann said on journalist Andy Ngo’s podcast. “It’s the groups, like to some extent the Mormons but definitely the Amish and the Ultra-Orthodox…they’re not out there proselytizing. It’s growing your own and walling yourself off from the modern world. That’s the most consistently successful evolutionary model for religious growth. And you retain the children in the fold. So you have a very limited loss of membership to the main secular society.”
Laurence R. Iannaccone’s 1994 study “Why Strict Churches Are Strong,” which has been frequently cited and confirmed since, gives more detail on the success of certain community codes.
Iannaconne found that groups can be strict on items as long as they provide a “close substitute.” Think, for example, of banning social media but then providing a lot of new in-person social opportunities to make up for that sacrifice.
“Strictness works,” he says, but the rules can’t be so strict they make people miserable and drive them away, or as Iannaconne says, “Arbitrary strictness will fail just as surely as excessive strictness.” The rules do have to be strong enough, though, to keep “free-riders” from claiming the benefits of the community without participating. He called these rules “costly signals,” like the sacrifices the Amish make by limiting their clothing styles and technology use. A person would be very unlikely to go through all of those costly steps for community benefits they could get more easily elsewhere. By eliminating free-riders—whose “mere presence dilutes a group’s resources, reducing the average level of participation, enthusiasm, energy, and the like”—they see the reverse, very high levels of participation, enthusiasm, and energy.
It’s not just Amish and Haredi Jews that have seen success with following a community code beyond the laws of the state—think of the monastics who survived in far-flung places relying on The Rule of St. Benedict; knights that followed the Codes of Chivalry; bands of cowboys on the American frontier who stuck close to the Code of the West, which gave detailed guidance on passing strangers on the trail, when to tip your hat, and with which hand you should hold your whiskey; and the tribes along the Afghanistan-Pakistan border who have followed the Pashtunwali code since pre-Islamic times.
It seems like a natural and prudent thing in lawless times and places to develop a code your community can thrive under. With Christians now living in a society where the customs and laws often violate our faith, it may be time to think of how we can band together locally under mutually agreed-upon codes too.
Modern Christians interested in starting a rule-based community would need to create some real benefits that are harder to come by in society at large. I’d suggest the basic benefits of a traditional community (help with childcare and schooling, coherent customs on dating and marriage, providing purpose and companionship to the elderly, cultural celebrations and gatherings, friendship, and assistance during hardship) would be plenty.
Then, they could agree together on some basic rules that are costly enough to separate the serious from the free-riders while not being arbitrary or unnecessarily strict. Targeting the rules toward areas that are particular downfalls for modern Americans (promiscuity, pornography, social media, screen-addiction, substance abuse) would be a good start. Agreeing to forego these in this time and culture would almost certainly be a costly enough signal.
Also, many of the rules should take into account issues like abuse of power, cults of personality, convenient personal revelations from God, sexual abuse, and a host of other issues inherent to tight-knit communities (and larger ones for that matter). The ability for a trusted leader to turn out to be an evil psychopath should never be underestimated, so rules should take that likelihood as a given and guard against it. The Amish, for example, draw straws to choose their leaders to avoid jockeying for power.
One last consideration is to what extent “walling yourself off from the modern world,” as Kaufmann said, is appropriate. Kaufmann said that was the best strategy for growth, but growth is not the only thing to weigh. There are also things like loving your neighbors, having an influence on the greater culture, and not stifling curiosity and creativity. Some walls are necessary, like between a teen boy and pornographic websites or between a child and an activist teacher, but a balance between walls and open spaces should be carefully pursued as a group. For example, language is used as a wall for the Amish (who speak Pennsylvania Dutch) and the Haredi Jews (who largely speak Yiddish), but that would likely be a step too far for most communities, as would their highly-detailed clothing restrictions.
So, these rules would naturally differ as people experiment, and best-practices would hopefully emerge.
Out-of-the-box? Sure. But with the exponential growth of the Amish and similar rule-based communities (and our own failure to find a workable model for modern Christian life) it may be a paradigm to consider. Even without our participation, it will certainly be how a fair amount of future Christians will live.
[Photo Credit: Unsplash]
